Table of Contents
Introduction
This digital literacies research or study is about and conducting with a view to examining the professional needs for the linguistics or language Learner’s and teacher of digital literacies. This article will explore digital literacies and language learners’ and teacher’s co- interrelationship. And will highlight the importance and fundaments of digital literacies. How will, can and being affecting digital literacies to language learners and for an instructor will be discussed in this article.
After reading this article you will be able to answer about, what is digital and digital literacies? What is the role of it in this world and today tech revolted time? Who are they and what are the roles of language learners and teachers in digital literacies and why it so important for them? Why this so important and necessary to survive in this competence world in every field? Will be discussed how safe secure online learning as well.
This will also encourage you to be a part of digital literacy and today’s mediated life and teaches you how you can play a vital role in it and make your place in this. In this will be disused about the means of digital literacies and available plate form to gain it, and all about its dimensions of work and thought.
This comprehensive study of digital literacies for language learners and teachers will consist and disuse the new technology, their importance, digital literacies effects on literacy rate, contribution towards the sociality and social media, creativity, interrelation with innovation and invention, mental level improvement and individual’s skills, ability, the strength of work. The digital-first time introduced by Paul Glister in 1997. He defined it as the ability of understanding of digitalized information and uses of it.
Digital literacies
Digital technology has significantly contributed to the shaping of an increasingly digitalized landscape of English language teaching (ELT) in today’s digital life. Literacy word referred to as the ability of some of the reading-writing, writing skills and communication with others. While digital literacies mean an ability to use the media or digital resources, information and communications with the help of the internet online to create, evaluate, communicate along technical and cognitive skills. (Heitin, 2016).
Digital literacies are very important for language learners and for the instructor as well. This can help them to enhance their ability and skills to meet this competitive time. Digital literacies can play a vital in increasing the literacy rate of any nation. Digital technologies are very faster resources now to get new and updated information with less than seconds after every second. This is becoming more populous in and demanded in developing countries because it is so cheap, available on the doorstep and far from just one click.
The uses of the computer also increased in a very short time in these countries. As language learners and teacher, it is no doubt that digital literacies can improve their communication, conservation and language problems, and skills. And can make them a good member of the digital world of today. Digital literacies are not limited by age, genre, class, wealth, sex, and individual patent. It a universal literacy opportunity for everyone. A person if he/she can operate the computer, mobile, radio and tv as well effectively, they can call digital literates.
The term digital literacies can be called shorthand and secondary optional opportunity of literacy or education. Digital literacy is very essential for the language and teacher, because by it they can behave well, talk and interact, be creative & innovative in their skills and knowledge, and can build a good relationship within their dimension and across of it. Digital literacies essentiality can be measured by these following 8 “C”.
| Cultural Confident Cognitive Critical Civic Creative Constructive Communicative |
In this competence and the digitalizing world, every student of language and instructor have to best in their skills and ability. They get literate about the above of functional IT skills and have to be on the top, not be the only user of it. Students, whatever they are langue learners, teachers or belong to any discipline have to be innovative, creative, differentiated and advanced in digital skills or literacy to compete and skiff off their rival in completion.
Figure 2 of Beetham and Sharpe’s pyramid (2010) can help the student as a teacher of language to do the development of his/her digital literacy. It can help the student of language and instructors as well to develop their digital skills for the functional to a higher level of capabilities. (Jisc, 2014)
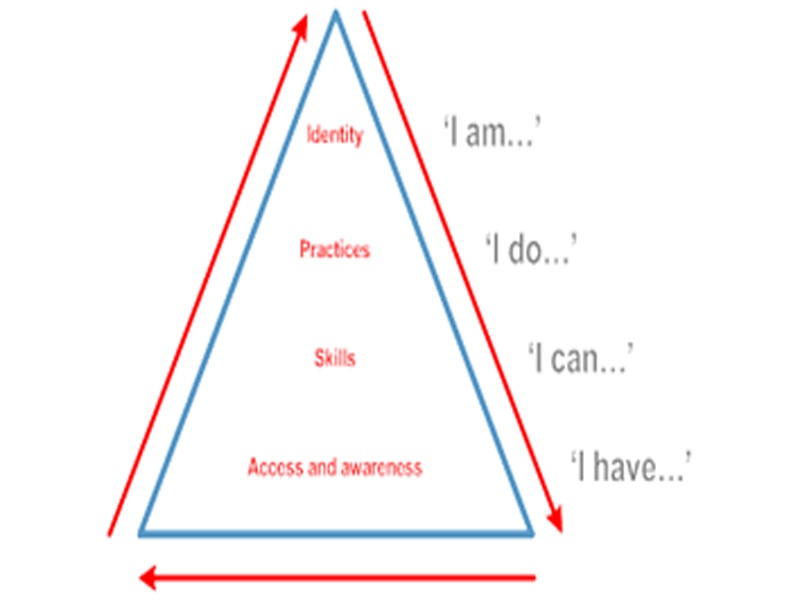
Digital literacies are those capabilities that are required to thrive, i.e. and be an effective and responsible participant, in a digital or mediated society. (Advance He, 2017). By the adoption of digital literacies, an individual can make a benchmark for others and be a role model for others in this modern era where are competency level is increasing day by day.
As per organizational and institute purposes and points of view, they can make their employee’s skills and ability and make the higher-level workforce of the organization to get their goal effectively. By this, these companies and organizations can do acknowledgment and professional development of their HR as well trained them according to the new technologies and equipment to do work faster and increase the productivity of both.
The professional development resources are designed to support primary and secondary school teachers to integrate the development of students’ digital literacy into everyday curriculum teaching and learning activities.
For advancing in the digital literacy competencies of educators, create opportunities for them to reflect on their motivations for using digital media, make collaborative inquiry a substantive component of the hands‐on learning experience, and create opportunities to put teachers and learners (not machines) at the center of attention. (International Literacy Association, 2018).
The following are the seven elements of digital literacies (figure 3) which encompasses how to live, grow, learn and work properly and with productivity in the digitalized world.
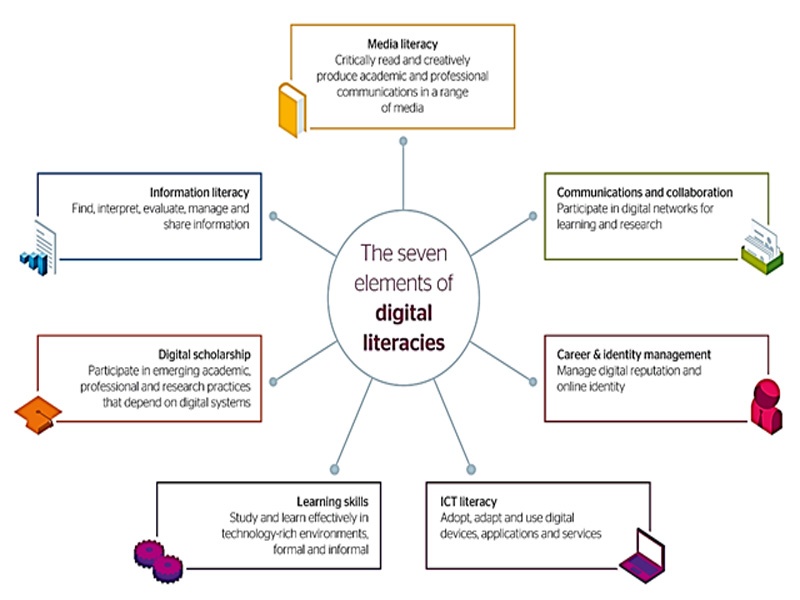
With all this framework literacies elements, an individual and organization can get to guide them. how they get involve their selves properly and effectively and how they are survival in the digitalized time. By this, a student, an individual; an organization, an institute can get success and higher positions in their field with quickly; cheaper, and easy to approachable resources.
These digital literacies can help them to build their critical thinking, identification of profession and its development; career/ goal identification and management; boost their learning skills, make better communication and collaboration each other, increase the chance and opportunities of digital scholarships to enhance their education and skills, and increase their literacy media literacies.
It provides ideas and resources to inspire the strategic development of digital literacies – those capabilities which support living, learning and working in a digital society. (JICS, 2014).
With the key concepts of digital literacies and new literacies, we can easily do distinguish between digital literacy and its components and clearly understands it. New literacies include traditional, informational; digital; Tools; mediated; critical, and visual literacies.
And digital components include functional skill, creativity; e-safety; effective communication; critical thinking and evaluating; ability to find and searching; collaborating, and understanding of cultural, social values or norms. Digital literacies involve more than the mere ability to use software or operate a digital device; it includes a large variety of complex cognitive, motor, sociological, and emotional skills, which users need in order to function effectively in digital environments. (Yoram Eshet, 2004)
In 2003, Martin introduced the term e-learning and referred to it as digital literacies in his article. This term was the first time launched by him for the digital literacies. Many other literacies under different names and terminologies are also exited apart from the digital and e-learning literacies terminologies. Some of them are the following:
- Technological literacy
- Digitized literacy
- Character encoding literacy
- Informative Literacy
- Media literacy
- Computer literacy
- Digital library
Digital term is like an umbrella that is compulsory to take all advantage of digital time. Who’s are literate with computer knowledge or any digital means of a source can get the all technical and information knowledge of the 21st century digital age of time. With this, they can improve their language problems, education; easily can handle finance problems; social life and make a bright future. (Yourdictionary, n.d.).
Digital literacies are very vast in size. It cannot be a spouse for only one person or community, class, or nation. Mobilizing, globally accesses, smartness, easy to handle, cheaper and 24/7 of 365 are the big advantage of it. This kind of literacies nourishes the individual, language communication, skills, and mental capabilities.
Digital literacies can do a vital role in professional skills development and productivity. It is becoming compulsory for the employees and students to have some interaction with digital literacies to survive and move forward in this fast and teach revolution time of history.
Four basic principles of digital literacies are being discussed follow, which are should follow be to be competent in the digital time or life. (see figure 4)
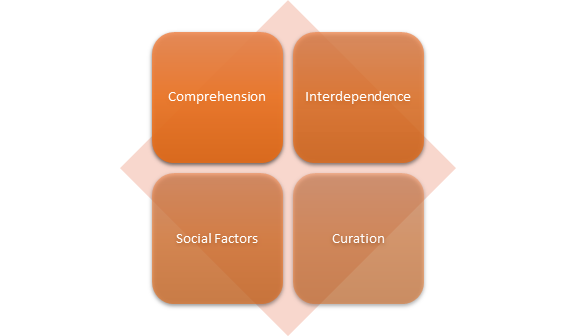
Comprehension:
It is compulsory to have comprehensive ability to extract, implies and explicit the data, information form the media for digital literacy.
Interdependence:
According to the second principle of the digital literacy that how, one means of media interconnects forms a connection with another one, whether do this by literally, metaphorically, identically. The purpose of the small type of media with isolation and easiness of publication is becoming so comfortable. This principle cam helps to stop a huge number of media to make co-exist, but not supplement each other by interaction.
Social Factors:
Sharing and distribution of information and ideas on social plate form are no longer as only personal identification methods. These media plate forms usage whatever they are cannot determine the success of them in the future, but they can make a social ecosystem of sharing, storing, resources, etc.
Curation:
This fourth and last principle of digital literacies, if a visitor or digital literate person make some action on some media plate forms such YouTube, Face book e.g. like as saving contents (videos on YouTube and posts on Facebook) for later watching or reading, indicate that, this is also a digital literacy. Because the visitor or user has the knowledge of how to overcome storage overflowing and digital hoarding. (Heick, 2015).
Literacy is viewed by some scholars as to the ability to interpret and construct meanings from various textual forms, like sounds, images and videos, games from websites and social networks. As a result, the definition of text goes beyond the conventional print media like newspapers, pamphlets broachers and visiting cards, etc., and embraces the digital technology to include text messages, photographs and visual graphics accessible from multiple digital media.
Digital Literacy and the language learner
This is a globally digitalized interconnected world, visitors and users of its identification are not fixed and durables and becoming lessor by the time of passage. Means and attitude on online of communication and commitments are powerful contributors towards the identification and formation.
Widely development of “Information and Communication Technology” (ICT) provides numerous opportunities and challenges for language learners. Participating in online communities and actives may require from its users that, they should develop their new skills, and improve the pre-exited. As well as they may need some software and hardware to utilize it, and they can learn and improve their behavioral conventions, traditions, and so-called norms.
In this passage, we will consider which are an essential element, what are their impact on ongoing new digital literacies needs and the requirement for competence on language learning and its practice as formally out of school instructive environment.
We will learn under this heading, how the learners can achieve language development and can gain literacy by being a part of the online participation of communities and such activities as informal language instruction sense. Engaging with online literacies media platforms involves the ability to create & provides remix information and materials from a variety of resources and sources.
Digital literacies can occur incidentally and that may be focused on language learning by participating in the internet in social or other communities and activates. By this they might abled to evaluate, search, collect information, data and avail the service online.
As a language student and instruct it is my obligation to encourage and motivate my students of a language learner to gain new skills, develop the professional ability, and become the matchless language learner on local or online communities as a responsible and reliable user and participant. Every child or student is different from each other on their capabilities, skills, intelligence, attitude and behavior.
A teacher is a responsibility to make them smile, give them the light of hope, helping them in learning and make sure they become successful, (Holland, 2016). The full range of the digital literacies can be referred to as capability in every field of life likewise, education, employment, and personal ability.
Learners need to learn how to combine both “Foreign language” “e-skills” or “new literacies” to be able to work and collaborate in new contexts between the visual and the real and between the distant and the proximate are increasingly blurred, (Godwin-Jones, 2015)
A language learner should have and can get improvement in his/her language thought through online activity and use-nesses and participating in online communities & activities. There unlimited benefits in an online learning environment for students. Five of them are below:
- Digital literacy boosts student engagement.
- Digital literacy improves academic performance.
- Digital literacy helps students stand out from their competition in the job market.
- Digital literacy makes your school more competitive.
- Driving digital literacy is easier than you think.
In this technological and digital world language learner and abundant sources of information, instruction plate forms, data’s, and material with full accuracy, authentication, and priceless quality to get learn language whatever it a foreign language or native. Even free and valuable is that by this they can interact and meet online with the authentic right person to who is learning and to whom he /she teaching the desired language.
Because illiterate or digital illiterate cannot survive there. Many authors and writers highlighted the impact of digital literacies on language learner social, culturally by committing them with online participating.
Language learners visiting online for language learning and development are increasing day by day. But some of the factors can affect it. According to Kathy Harris, ELLs and their teachers are parts of digital literacies, experience, and skills. Education, age, income, access to technology, social networks, and family members are some of the many factors that influence the digital literacy of ELLs. (Kathy Harris, n.d.)
They are independently availing these opportunities fearlessly on online by making a connection with others. They have and taking advantage of free usage of their own text, visual in their own language and of other languages.
Internet or digital literacy resources with easy availability increased the ratio of language learners in the past few years. Innovation and invention in technology also make an impact on it. Recently studies evaluate that, usage of internet, radio; Tv; voice text, and video chat and MMS has been increased in huge quantities.
Globally availability of the internet or digital literacies made the spark on languages learner experience typically increased in multilingual and multi and mix cultural contexts. They have leading and better choices in linguistics and culture learning. In our modern world, digital literacy means changing after every second due to continuous innovation and inventions in technology.
So the learner of language should be kept in touch with the internet to improve his/her skills of language, communication. As a student of language, he/ she must be able to match the required responsibly toward him/her of digital society and for a successful future. According to the US Bureau of Labor 77% of jobs within the next decade will be required some degree of technology skills. (OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS, 2017).
Some studies indicated that, if students of language do participate online independently their performance and productivity improved than before. (MojganAfshari, 2013). Some cases showed the feeling of alienation of students in classes.
Participating in an online framework increases the chances of trying to play different roles and by paying some responsibilities, taking different identities which can train them to react in a good manner in the digital literacies era.
Language students can perform them by a new language, taking risk of being a laugh in face-to-face dialogue situations or in class. Students of level tow can get about the experience of conventional and non-conventional forms of different languages and rules of online participating in a variety of communities and taking part in learning activities.
Distance learning and independent learning improve digital ability along with his/her literacies. A study showed that students felt more comfortable in out of classrooms and online learning rather than in the class. It does impact on their confidence, attitude, and language.
There is considerable evidence that using technology as an instructional tool improves student learning and educational outcomes (Shana, 2009). A language learner should follow and work through these five basic essential digital skills framework. (see figure 5).
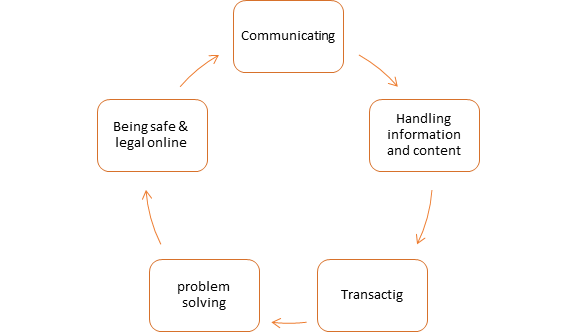
This framework was designed for the support of online limited workers and visitors across the UK, but they can help out the language leaner across the world for all adults and for preventing their essential digital skills, skills, information, and data and perform in the digital world well.
The framework has been named for the new national standards for essential digital skills in 2019. (GOV.UK, 2018). In linguistic literature field more specifically in the language and technology interrelation context, we found and identify two aspects of digital literacies: (see figure 6)

1: New Needs of language learners:
According to this aspect that new ideas, innovation, and new inventions in means of communication, digital literacies of reading, writing should create and be addressed in level 2 and FLL education.
2: New Context of language learning:
Online communities and activities participating make an autonomous space for the opportunities for language teacher or instructor who wants language learning in multicultural and in the multilingual sense of contexts. That contribution to phenomenal theme out of classroom environment learning first of language learning or instructor and its practices, and later its integration
Digital Literacies and the language teachers
Digital literacies in language instruction are so important, in this digital age their collaboration is very necessary to make a well educated, digital skilled and literate youth for living in the Social-Digi environment. It is a duty of language instructor to solve out all problems of his/her students to survive, competent, better communicators online.
Digital literacies are the required part of today’s world teaching style. As a language instructor, he/has so many liabilities on their shoulder make a competent generation of this tech time. By this the can payed their responsibilities as a member of the digital. Following 7 reasons can help out in understanding the needs of digital literacies for the language teacher. (see figure 7).
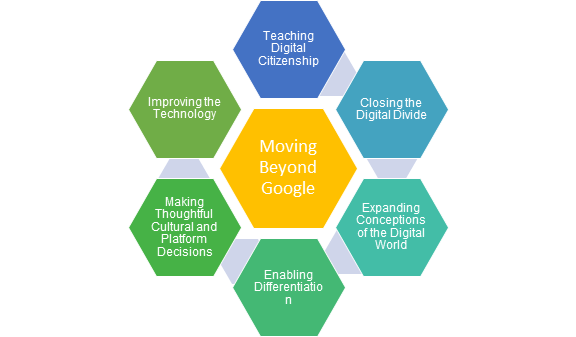
It makes sense to assume that the more digitally literate our teachers are, the more they’ll employ these skills in the classroom, which will in turn foster a strong sense of digital citizenship in our students. (Levy, 2018). Digital literacies are integrated with each other; they cannot have thought separately. (Webber, 2017).
Due to globalization in digital literacies and education many students came from a different nation and speaks different languages, they may face problems in getting instruction from his/her instructor whatever he/she is language teacher or not. So, the instructors or teachers can modify their language abilities with digital sources to be better in communicating and teaching to his/her learners.
This essential for the language teacher to have some kind of digital skill. This can help her/his out to move forward in this binary time and grow. A teacher may improve their skills, update their knowledge day by day and inspire the students of language learners too.
There is no argument in training the students for skills that, will be obsolete by the time when they start working or participating in online communities and activities. It is key for the teachers, that we are future-focused and helping students in the preparation of this ever-changing digital society. (Roslaniec, 2018). We can analysis digital literacies importance role and responsibilities toward a language teacher by tow followings:
DIGITAL PRACTICES AND THE LANGUAGE CURRICULUM
Digital practices and the language curriculum enhance teaching or learning through effective use of digital technology by engaging curriculum design: Strategies are focusing on design, development; technology integration; and providing undergraduate language courses. (GeddesLanguageCenter, n.d.)
Needs, responsibilities, and demands from the language learner are increasing day by day because of the ever-changing digital era now to remodify and develop their language curriculums and ways of teaching from the so-called to digitalized ways to full fills the all-digital literacies need of the language learner.
According to the European Center for modern languages of the council of Europe, as language is at the root of all learning, there can be no quality education without quality language and intercultural education.
All teachers, at all levels, whatever subject they teach, have an important part to play in building their learners’ linguistic and intercultural repertoires. (European Center for modern languages of the council of Europe, n.d.). For the effectiveness in his work, a teacher should keep growing his/ her education and skills to meet up the job Desir nesses and he/she should be authentic in knowledge, skills in online communities.
The following aspect can be helpful for him/ her to be competent, and move forward in digital life and enhance digital literacies for the language students or learners. They are being disused below:
- Should be an autonomous learner
- Should be attractive and effective in FL learning and understanding
- Digital literate
- Have a place in professional communities and practicing it
- Competent as a languages teacher
- The “CEFR”
- Self-testing and assessment
- Pre or early languages learners
- A multilingual and intercultural approach
- Holistic learner
Online authenticity is very important for the teacher and for the learners of the language. How? What? and Why? It can be called the main tool to be in safe mode. The text should be followed through them,( American council on the teaching of a foreign language), (ACTFL, n.d.). So the students will be asked to him the reliable source for the more information and their selves research about the language and its practice.
A language teacher should have authentic and reliable sources to admire them to reach. Such as Wiki, YouTube, Facebook, etc. Computer and mediated pedagogy of literacies are becoming popular globally. These can be called simple tools to enhance the capabilities of language learners and teachers by participating in it.
They can increase their efficiency, grow interested; get teach the management of work fast and compete with others. (Edwards, 2014). So by nature, effective classrooms are their parties totally depends on teachers’ digitally literacies, skills, and self-experience. Language teacher who has had the experience and digital skills at a higher level, it is cannot necessary for practices in the class.
Ekaterina tours contributed to this to evaluate the interconnection between the teacher or instructor’s personal and professional skills usage of digitally. It provided the trice language instructor result by investigating them by open interview, visually and self-analysis to figure out their practice of digital literacies inside or outside the class environment.
This research also resulted in the affordance capabilities of the teacher, that they can afford the digital tools or not practice it. It also highlighted and proved that digital literacies are very useful to enhance and nourish the language teacher exited skills to compile with a modern way of teaching.
All this showed that there is also a need for the mind-set of the language to acquire digital literacy techniques and adoption too. And competent trainees to trains the teacher, how they can utilize the digital literacies.
Curricular integration
Learning is also possible through the physical exits in document forms likewise, books, journals, magazines, and newspapers to fill the language practice and learning curriculum needs. Thorne & Reinhardt’s theory of bridge activates for the language learning and teaching provide a well-organized way of out of class environment and means of online participating to students find and evaluate the resources of their interest independently.
Digital literacies are a goal for every language stakeholder, nearly. The evidence of student knowledge, skills and abilities may be assessed via student sub missioning of documenting showing activities, rather than via so-called and formal assessments technique or by requiring short time courses.
Students demonstrate an ability to use a variety of online tools and services, participating in online communities is the widespread use of learning management framework. For making every learner and seeker students, the teacher should have to keep practicing their digital skills and abilities. That must admire them as well.
Curricular integration is very important for the students to meet the set standards of learning. Another lee a professor of the University of Miami did a project with elementary levels students of a wind machine. After the project completion, it indicates that students became more idealistic than before started thinking broadly, because of curricular integration among them and between her and them. (Burns, n.d.)
Challenges with integrating online practices in formal classroom settings
For many years’ students are likely forcing to gain their knowledge by their own self-research and participating in online activities and communities, for example in a social environment such as Facebook, YouTube, etc. and on many other social activist websites or the use of online media.
In multi and effective productivity and implementing of online language learning they still need guidelines and training, technology tools and environments offer students more control and support than traditional learning settings, explicit training is valuable in helping them to use that technology more effectively (Philip Hubbard, 2018).
The trice-tiered framework of Hauck, Mirjam, and Kurek, Malgorzata for the multilateral training of the language learner can help out for training of students to doing their job effectively and efficiently, enable them to do things independently and move along technology-mediated and do contribution of multimodal outputs (Hauck, 2014).
It shows language development from observation and fully participating do well instead of just learning the environment. They indicate that students never ever stop to literate their selves, for moving and living and being an active member of digital society it is compulsory.
The teacher guideline is very important for the learner; it may require at any time from the students. Online practices in formal classes must be according to the level of the learner. Simplification in teaching is necessary for the best output of language learners.
Further issues: how to stop considering digital literacies as fun and how to assess them
As a whole, the contributions to this phenomenon focus on important features of digital literacies, if we talk about language learning. They help us to understand the nature of digital practices. We must take steps to apply digital literacies into language learning.
It is also clear that the adventure of rethinking the curriculum to take digital literacies into account is becoming increasingly important. We know that it is urgent to overcome the hurdles in this way of advance learning. If it becomes a classroom practice, there is a little hope about assessment. But there is the only problem how student’s participation in an innovating digital practice can be assessed as described by the king in the best way.
A related problem is that public examinations remain largely unchanged in regard to relevant national language and literacy standards. Until such a high accelerating examination is alliterated, most of the teachers are inclined to continue to perceive digital literacies as more of a helping tool than a compulsory part of the traditional curriculum.
When we unlock the myriad learning opportunities in globalized inline space, out of the classroom environment, it requires actively participating in such spaces. Research has shown to us very clearly that learners take the adventure of a variety of unstoppable spaces. It is also true that participation lies upon the opportunities of access.
But it is also a fact that promotion doors to access are poorly understood. What should be the role of society? What are the factors so far informal mentoring? How can we make or empower that active participation of the learners to take advantage of learning the language? These and many other questions lie ahead to push us to move a better and correct understanding of digital literacies and language learning.
Conclusion
All above these talks brings us on one thing and thought that where everything is coming online and digitalizing itself. An individual what he/she is a student or teacher of any kind of subject, it is compulsory for them to get literate their selves with digital literacy. Without this, they cannot survive longer.
As language learners or instructors, it becomes more valuable for them that they can improve their language problems with no time at just one click or touch, and give them breath to move, work independently in this fast-changing world.
The obligation also on their shoulder to be a part of the online communities to help out them who are left behind and have no source of digital literacy as well, and that definitely helps them out to practice of their communication, problem-solving; evaluating, and becoming an authentic user or community personality of digital societies.
References
ACTFL. (n.d.). USE OF AUTHENTIC TEXTS IN LANGUAGE LEARNING. ACTFL
Advance He. (2017, 5 18). Digital literacies. head academy
Belshaw, D. (2015, 4 27). Open Networked Learning: Digital Literacies with Dr. Doug Belshaw.
Burns, S. M. (n.d.). Meeting Standards Through Integrated Curriculum. ASCD
Edwards, R. (2014, 12 12). Software and the hidden curriculum in digital education. Taylor&FransicOnline
Europeans Center for modern languages of the council of Europe. (n.d.). Languages at the heart of learning. ECML
GeddesLanguageCenter. (n.d.). Digital Strategy for Teaching and Learning Languages at Boston University. BU
Godwin-Jones, R. (2015). Contributing, Creating, Curating: Digital Literacies for Language Learners. Language Learning & Technology, v19 n3 p8.
GOV.UK. (2018, 9 12). Essential digital skills framework. EDSF
Hauck, M. a. (2014, 1). Closing the digital divide-a framework for multiliteracy training. in book.
Heick, T. (2015, 11 21). 4 Principles Of Digital Literacy. teaching thought
Heitin, L. (2016). What Is Digital Literacy? Digital Literacy: An Evolving Definition.
Holland, J. (2016). Digital Literacy and English Language Learners. Retrieved from Slide player: https://slideplayer.com/slide/6349671/
International Literacy Association. (2018, 9 19). Design Features of a Professional Development Program in Digital Literacy. ila
JICS. (2014, 3 6). Developing digital literacies. JISC
Jisc. (2014, 3 6). Developing digital literacies. JISC
Kathy Harris, P. S. (n.d.). Integrating Digital Literacy Into English Language Instruction. LINCS
Levy, L. A. (2018, 7 25). 7 Reasons Why Digital Literacy is Important for Teachers. USC Rossier
MojganAfshari, S. (2013, 11 26). Students’ Attitudes towards Computer-assisted Language Learning. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, pp. 852-859.
OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS. (2017, 1 31). Digital literacy: the missing piece for Adult ESL learners. oupeltglobalblog
Philip Hubbard. (2018, 1 18). Learner Training. Wiley online library
Roslaniec, A. (2018, 6 15). Digital literacy and secondary education. Pearson
Shana, Z. (2009). Learning with Technology: Using Discussion Forums to Augment a Traditional-Style Class. Educational Technology & Society, 12(3):214-228.
Webber, A. A. (2017, 8 8). Integrating Digital Literacy and Language Instruction. EdtechCenter
Yoram Eshet, T. H. (2004). Digital Literacy: A Conceptual Framework for Survival Skills in the Digital era. Journal of Educational Multimedia and Hypermedia, Volume 13, Number 1.
Your dictionary. (n.d.). digital literacy – Computer Definition. YD

