HTTP requests are binary information packets that a computer or client sends to another computer or server to communicate.
Table of Contents
What is routing in Express JS?
Routing is basically defined as the process of selecting a path for traffic or request in a network or in a web framework. In Express JS, we can access web pages, files, images, scripts, stylesheets etc. at different paths set by route. To define a route in Express, we use app.method (path, handler).
app.method (path, handler)
This is a function which is used to define various routes for different types of requests. Path is address of route and handler is the function which will receive the request and give response to that request.
HTTP Requests Methods in Express JS
Types of Request Methods for Routes (app.method(path, handler))
| GET | It is used when data fetching is required from server for representation on client side. |
| POST | It is used when |
| PUT | It is used to store and update data. If an object exists already, it updates or modifies it. If the object does not exist, it creates new. |
| DELETE | It is used to delete data from server. |
Examples of GET & POST Requests in Express JS
Let’s take an example of a /home route. In this example, we have defined a route at http://localhost:3000/home. The server receives get type request when we access this address. After receiving
//imports express module
let express = require('express');
//initializes express app
let app = express();
//creates get function with request and response parameters
app.get('/home', function(req, res){
//sends response to client or browser
res.send("Welcome to Homepage");
});
//listens to server at port 3000
app.listen(3000);
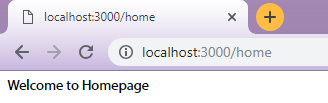
After accessing http://localhost:3000/home, you will see the following response on
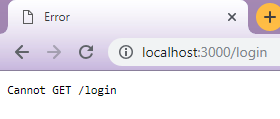
Now just try to access different routes without defining. For example, we haven’t defined any route in above code for path /login. You will see Cannot GET / Login response on requesting this address.
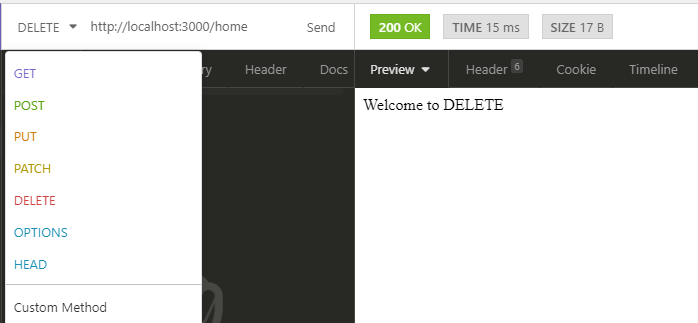
Now to check
GET and POST Requests in Express JS
Let’s take another example by defining GET and POST request at same route.
//imports express module
let express = require('express');
//initializes express app
let app = express();
//creates get function with request and response parameters
app.get('/home', function(req, res){
//sends response to client or browser
res.send("Welcome to GET");
});
//creates post function with request and response parameters
app.post('/home', function(req, res){
//sends response to client or browser
res.send("Welcome to POST");
});
//listens to server at port 3000
app.listen(3000);
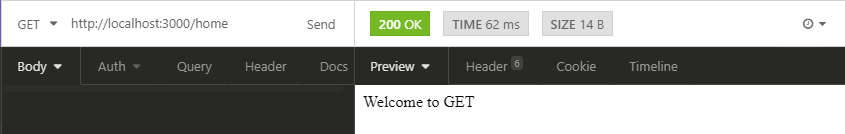
GET Request Output in Express JS
When you will access /home route with
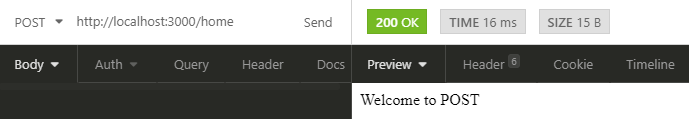
POST Request Output in Express JS
But when you will access /home route with
PUT & DELETE Requests in Express JS
Similarly, modify the code to check PUT and DELETE request.
//imports express module
let express = require('express');
//initializes express app
let app = express();
//creates get function with request and response parameters
app.delete('/home', function(req, res){
//sends response to client or browser
res.send("Welcome to DELETE");
});
//creates post function with request and response parameters
app.put('/home', function(req, res){
//sends response to client or browser
res.send("Welcome to PUT");
});
//listens to server at port 3000
app.listen(3000);
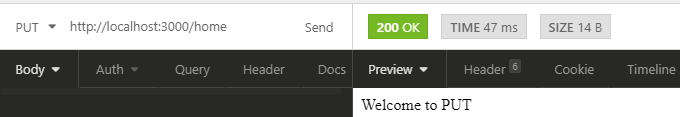
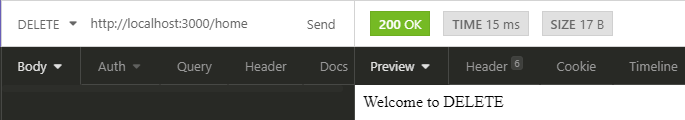
You will see Welcome to PUT response for your PUT method route and Welcome to DELETE response for your DELETE method route.
Outputs for PUT & DELETE Requests
All requests route in Express JS
In some scenarios, we have to use all the methods for a single route. For example, in middleware, we use this. Look at the code below, it has a route with all method. It will respond to all HTTP requests. The response will be same for all HTTP requests no matter it is GET, POST, DELETE or PUT.
//imports express module
let express = require('express');
//initializes express app
let app = express();
//creates all function with request and response parameters
app.all('/home', function(req, res){
//sends response to client or browser
res.send("Welcome to Home");
});
//listens to server at port 3000
app.listen(3000);
In the next tutorial, you will learn how to add static and dynamic routing in Express JS.

