Parts of speech are a way to describe the functions of words in English language.
Table of Contents
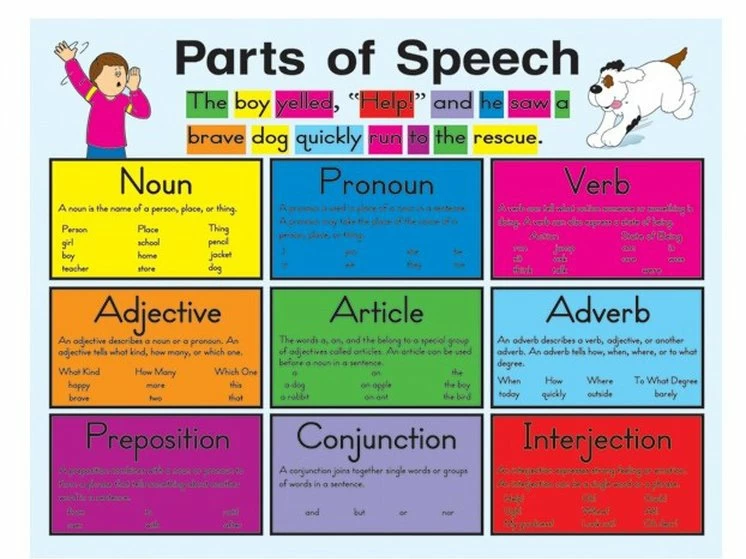
Parts of Speech Diagram
There are 8 parts of speech.

LESSON NO 1
NOUN
Definition:
A noun is a word that is used for some person, place, thing, state, idea or action. They are of different kinds.
Types of Nouns:
There are six types of nouns:
1- Proper Noun
The name of a particular person, place or thing is called proper noun e.g. Gujranwala, Mount Everest, The United States, Keats, Shakespeare, etc.
2- Common Noun
The name of a common person, place or thing is called common noun e.g, pen, book, man, garden, chair, table, church, etc.
3- Abstract Noun
A noun that denotes some quality, state, idea or action is called abstract noun. Friendship, music hatred, love, ugliness, truth, death, sobriety, pride, bravery, growth, belief, wisdom, beauty, etc.
4- Material Noun
A noun that denotes the matter or substance of which things are made is called material noun e.g, wheat, rice, curd, milk, wood, etc.
5- Collective Noun
The name of a group of things of beings or things is called collective noun e.g, public, people gentry, poultry, team, police, class, etc.
6- Compound Noun
When two or more than two words join together, they are called compound nouns e.g, lady-doctor, step-brother, class-fellow, chair-person, etc.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 1
Fill in the blanks with right name of the noun
- –———————— Cowardice
- ————————- Intelligence
- ————————- Public
- ————————- Gentry
- ————————- Passer-by
- ————————- The Indus
- ————————- Cattle
- ————————- Police
- ————————- The Earth
- ————————- OX
- ————————- Tooth
- ————————- Butter
- ————————- Love
- ————————- Mosque
- ————————- Shakespeare
- ————————- Dr. Morlow
- ————————- Rain-bow
- ————————- Reality
- ————————- Rice
- ————————- Wood
- ————————- Thief
- ————————- Major-General
- ————————- Party
- ————————- Gallon
- ————————- Toy
- ————————- Chair
- ————————- Bravery
- ————————- Effect
- ————————- Photo
- ————————- Tree
- ————————- Horse
- ————————- Life
- ————————- Saudi-Arabia
- ————————- Birth-day
LESSON NO 2
How to make and what are the rules to make plurals noun?
1. The plural of a noun is usually formed by adding, S as Book, Books, Girl, Girls, Toy, Toys, Boys, Boys, Chair, Chairs; Table, Tables, Pen, Pens, etc.
2. Words ending ch or sh, are made plurals by adding es, as church, churches, bench, benches; dish, dishes.
3. Words ending in-Y (if there is a consonant immediately before Y) Y is changed into i and es is added as Family, Families; Century, Centuries; Story, Stories; Body, Bodies; City, Cities, etc.
4. Words ending in F or FE most of these change F to V and add as Leaf, Leaves; Wife, Wives; Calf, Calves; Thief, Thieves; Hence following nouns ending in F or Fe take S after them to form their plurals. Safe, Grief, Chief, Roof, Hoof, Cliff, Dwarf.
5. Words ending in O take es after them to form their plurals, like Mango, Mangoes; Hero, Heroes; Innuendo, Innuendoes; Volcano, Volcanoes; Tomato, Tomatoes, Hence photo, Kilo, Piano, Gratto, Dynamo, Folio, Take, only S to become plural.
6. Words ending in is usually change is to es as Basis, Bases; Thesis, Theses; Synopsis, Synopses; Synthesis, Syntheses, etc.
7. Words ending in X are required es to make plurals as Box, Boxes; Tax, Taxes; etc.
8. Words end at S or SS are required es to make plurals as Bus, Buses; Ass, Asses; Glass, Glasses; Mass, Masses.
9. The following nouns have the same form in both numbers, Sheep, Fish, Trout, Swine, Heathen, Deer, Salmon, etc.
10. News, hair are plural nouns but they take a singular verb, as His hair is white. What is the latest news?
11. The following words have no plurals and are always used in a singular sense. Permission, Music, Pity, Scenery, Information, Machinery, Knowledge, Silver, Gold, Progress, Leisure.
12. These nouns are used as the plural in sense, Though look singular, Cattle, Gentry, Public, People, Police, Poultry.
13. These nouns are used as singular though look Plural, Innings, Physics, Statistics, Summons, Gallows, Politics, Mathematics.
14. These words may be made plural as:
Advice Pieces of advice
Abuse Words of abuse
Mischief Acts of mischief
15. These words are used as given (in either sense) Mustaches, Spectacles, Tongs, Trousers.
16. Words clothes are always used in plurals sense.
17. Wages are plural in a sense payment for work (also used sing. That is paid for services).
18. Some nouns are exempted from these rules.
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural |
| Tooth | Teeth | Formula | Formulas |
| Foot | Feet | Larva | Larvae |
| Man | Men | Bacterium | Bacteria |
| Woman | Women | OX | Oxen |
| Child | Children | Stratum | Strata |
| Goose | Geese | Testator | Testatrix |
| Mouse | Mice | Medium | Media/Mediums |
| Genus | Genera | Ovum | Ova |
| Louse | Lice | Bureau | Bureaux |
| Beau | Beaux | Curriculum | Curricula |
| Pupa | Pupae | Memorandum | Memoranda |
| Criterion | Criteria | Syllabus | Syllabi, Syllabuses |
| Erratum | Errata | Datum | Data |
EXERCISE OF LESSON 2
Make Plural From The Followimg NOUNS
Page, OX, Medium, Foot, Mass, Class, Witch, Inch, Wish, Story, Category, Century, Chief, Thief, Buffalo, Potato, Crisis, Halo, Loaf, Half, Box, Class, Cliff, Grief, Sky, Wolf, Bacterium, Datum, Clergy, Photo, Table, Word, Safe, Louse, Formula, Syllabus, Class-fellow, Brother-in-law, Sash; Ditch, Branch, Bench, Business, Spy, Library, Penny.
LESSON NO 3
PERSONAL PRONOUNS
Definition
A pronoun is a word that is used in the place of a noun or noun phrase.
They may be grouped into three categories.
1.Nominative (Subjective)
2. Possessive (Genitive)
3. Objective (Passive) (Accusative)
| I | II | III |
| Nominative | Possessive (Genitive) | Objective (Passive) (Accusative) |
| I | My, mine | Me |
| We | Our, ours | Us |
| You | Yours, you | You |
| She | Her, hers | Her |
| It | Its | It |
| They | Their, theirs | Them |
| He | His | Him |
For the use of Possessive Pronouns look at the following sentences.
| This is her book. | This is hers. |
| These are my pencils. | These are mine. |
| That is your bag. | That is yours. |
| That is our box. | That is ours. |
| It is my dog. | It is mine. |
| These are their books. | These are theirs. |
| Those are your toys. | Those are yours. |
LESSON NO 4
Relative Pronoun
These are used to relate a noun or a sub-clause to the main clause and serve as conjunctions, e.g.
Who, Whom used for person or persons.
Whose, That used for persons or things.
Which used for animals or things.
What, But, As are also relative pronouns.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 4
Complete these sentences with relative pronouns.
- I do not like such men _________________ deceive their friends.
- God helps those _________________ help themselves.
- All _________________ glitters is not gold.
- God loves those _________________ love their fellowmen.
- The man _________________ address you are asking is not here.
- The boy _________________ you want to meet has left this city.
- The cow _________________ you have bought is not healthy.
- She is a poetess _________________ her poems are very famous.
- You may take _________________ you like.
- _________________ you sow, so shall you reap.
LESSON NO 5
DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUN
The demonstrative pronoun points towards the noun it replaces, indicating it in time, space, and distance. They are This, That, These, and Those.
For example
- Near the speaker _________________ This and These will be used.
- Not at near the speaker _________________ That and Those will be used.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 5
I. Use This or These
- _________________ Page
- _________________ People
- _________________ Church
- _________________ Money
- _________________ Children
- _________________ News
- _________________ Bench
- _________________ Ladies
II. Use That or Those
- _________________ Girls
- _________________ Radio
- _________________ Man
- _________________ Men
- _________________ Women
- _________________ Dress
- _________________ Apples
- _________________ Student
LESSON NO 6
VERB
Definition
Verb is a word that denotes an action or activity of a person or thing. They are of three classes.
1. Transitive Verb
A transitive verb requires an object to complete its meaning.
Examples
- He is writing a letter.
- The mother looks after the children.
- I love my country.
2. Intransitive Verb
An intransitive verb expresses a state or action which affects the subject only.
- He is listening.
- He runs.
- They are weeping.
- He goes.
3. Helping Verb
The word which plays the role of linking or helping in a sentence is called helping verb.
It includes: Is, am, are, was, were, had, has, have, can, could, would, should, may, might, ought, will, shall, must.
FORMS OF VERB
Every verb has three forms. The first form is called infinitive, the second form is called preterite and the third form is called past participle. Hence, present participle (ing form) is also accepted as one of the form of the verb.
In most cases, ed is put to make the past of a verb. Hence, there are many irregular verbs. A list of these verbs is as.
| PRESENT | PAST | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| Bring | Brought | Brought |
| Build | Built | Built |
| Buy | Bought | Bought |
| Choose | Chose | Chosen |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk |
| Eat | Ate | Eaten |
| Feel | Felt | Felt |
| Find | Found | Found |
| Fly | Flew | Flown |
| Give | Gave | Given |
| Forgive | Forgave | Forgiven |
| Hear | Heard | Heard |
| Know | Knew | Known |
| Leave | Left | Left |
| Ride | Rode | Ridden |
| Say | Said | Said |
| Ring | Rang | Rung |
| Sleep | Slept | Slept |
| Take | Took | Taken |
| Teach | Taught | Taught |
| Tell | Told | Told |
| Wear | Wore | Worn |
| Write | Wrote | Written |
| Begin | Began | Begun |
| Blow | Blew | Blown |
| Break | Broke | Broken |
| Fall | Fell | Fallen |
| Get | Got | Got |
| Hide | Hid | Hidden |
| Hold | Held | Held |
| Lead | Led | Led |
| Lend | Lent | Lent |
| Win | Won | Won |
| Has, have | Had | Had |
| Lose | Lost | Lost |
| Make | Made | Made |
| Mean | Meant | Meant |
| Meet | Met | Met |
| Pay | Paid | Paid |
| Run | Ran | Run |
| Do | Did | Done |
| Feed | Fed | Fed |
| Sit | Sat | Sat |
| Think | Thought | Thought |
| Throw | Threw | Thrown |
| Understand | Understood | Understood |
| Steal | Stole | Stolen |
| Catch | Caught | Caught |
| Write | Wrote | Written |
| Tear | Tore | Torn |
| Slide | Slid | Slid |
| Come | Came | Come |
| Tell | Told | Told |
| Spin | Spun | Spun |
| See | Saw | Seen |
| Lay | Laid | Laid |
| Lie | Lay | Lain |
Note:
Spellings of some verbs remain the same in three forms as:-
Cut, put, spread, quit, fit,let, hurt, bet, shut, cast. Verb ending in Y if there is a consonant before y, y is replaced by ied in second and third form as.
| Marry | Married | Married |
| Carry | Carried | Carried |
| Bury | Buried | Buried |
| Try | Tried | Tried |
| Cry | Cried | Cried |
| Fry | Fried | Fried |
LESSON NO 7
ADJECTIVE
Adjective is a word used for qualifying the meaning of a noun or pronoun.
Definition
There are two types of adjective especially mentionable.
1. Adjective of Quality
When an adjective states the kind of the noun it qualifies, it is said to be an adjective of quality. For example; Tall boy, Beautiful girl, Black cat, Good student, and Bad man, etc.
2. Adjective of Quantity
When an adjective states the number or quantity of noun it is called an adjective of quantity .eg, how many, how much, third group, first meeting, last chance, and many girls, etc.
There are three degrees of an adjective.
Degree of Adjective
1. Positive Degree
It simply expresses quality as Week, Poor, Dark, Bright, Coward, and Pretty, etc.
2. The Comparative Degree
It is used to compare a thing or person with another; as, More, Poorer, Wiser, Higher, and taller, etc. Than is used with a second degree of an adjective.
3. Superlative Degree
It is used when a person or thing is superior to all others in a particular quality as, Poorest, Best, Most, Darkest, Smallest, Richest, and Latest, etc. The is used before the superlative degree of an adjective. Of is used after the superlative degree of an adjective.
Note:
The general rule to make a comparative degree and superlative degree, we put er or est with the positive degree of an adjective. However, here are some irregular adjectives exempted from the above-mentioned rules. They are:
| Positive Degree | Comparative Degree | Superlative Degree |
| Good | Better | Best |
| Bad | Worse | Worst |
| Far | Farther | Farthest |
| Much / many | More | Most |
| Little | Less | Least |
In case of other adjectives more and most are used before them for making comparative and superlative degree. As,
“Difficult: more difficult; most difficult”, “Beautiful; more beautiful; most beautiful”. To is used with inferior, superior, junior, senior, prior, and elder, etc.
LESSON NO 7
ADVERB
Definition
An adverb is a word used for qualifying the meaning of verb, adjective or other adverb. According to their meaning, they can be grouped in the following categories.
i. Adverb of Manner/ Quality or State
It indicates how the action takes place. As;
- She weeps bitterly.
- He can read it clearly.
- He appears suddenly.
- They eat them quickly.
ii. Adverb of Place
It indicates where the action takes place. As;
- What are you doing here?
- We will go there.
iii. Adverb of Time
It denotes when the action takes place.
- We used to play hockey daily.
- She has already left this city.
- She met me yesterday.
iv. Adverb Order
In a normal sentence, the adverb manner comes first; it is followed by the adverb of place and then comes the adverb of time; as “Sabiha stood first in the annual examination last year”.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 8
Here is a list of adverbs. Fill in the blanks with these given adverbs.
Clearly, recently, surely, sweetly, already, just, yet, happily, strangely, where, somewhere, immediately, luckily, quickly, apparently, certainly, proudly, slowly, comfortably, soundly, easily, fluently, elegantly, warmly, presently, suddenly, bravely, and rightly, etc.
1- Please speak _________________ .
2- I am _________________ going there today.
3- The air smells _________________ .
4- They have _________________ gone there.
5- He has not finished his work _________________ .
6- He has __________ joined this college.
7- I have _________________ shut the door.
8- Shahid has _________________ taken one cup of tea.
9- He has not _________________ completed his work.
10- He accepted my offer _________________ .
11- They sang _________________ .
12- Your story seems _________________ .
13- I went to the village _________________ I was born.
14- He kept his purse _________________ .
15- I can read quite _________________ .
16- _________________ I have passed the examination.
17- _________________ he is in the wrong.
18- He is sitting _________________ in the chair.
19- I drive my car _________________ .
20- He is sleeping _________________ .
21- I can drive _______________.
22- she can speak English _________________ .
23- She dresses _________________ .
24- Did we receive our leader _________________ ?
25- Type this letter _________________ .
26- The dog was beaten _________________ .
27- He solves the question _________________ .
28- _________________ he is coming _________________ .
29- He disappears _________________ .
30- They fought _________________ .
LESSON NO 9
Preposition
Definition
A preposition is a word used before a noun or a pronoun to show its relation with another person or thing. Examples on, in, of, off, up, into, over, under, after, about, against, below, at, with, to, by, for, since, from, upon, through, along, and above, over.
Some Solved Examples
He is ashamed of his behavior. 2. He is looking for his book. 3. Mr. Riaz is very popular with his students. 4. The patient is being operated upon. 5. They were running after a thief. 6. He is hidden behind a tree. 7. Divide these mangoes among all the boys. 8. Divide these apples between two brothers. 9. Open your book on page ten. 10. He writes in red ink. 11. I congratulated her on her success. 12. He does not care for anyone. 13. Always keep to the left. 14. Sidra works according to the time table. 15. I am thankful to you. 16. He will take revenge on you. 17. Hard work is the key to success. 18. You should not be indifferent to your studies. 19. Who will succeed to him? 20. I introduced him to my friends. 21. Is there no remedy for this disease? 22. Solve this sum within ten minutes. 23. She looks after her children. 24. He has no control over his feelings. 25. Saif lives at Sultan Pura in Gujranwala.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 9
Fill in the blanks with a suitable preposition:
You will succeed if you act _________________ my advice. 2. I am short _________________ money these days. 3. This cloth is inferior _________________ that. 4. _________________ God, we trust. 5. I shall receive my father _________________ the station. 6. The principal accepted _________________ my request _________________ leave. 7. His health is improving day _________________ day. 8. He has escaped _________________ the jail. 9. He has no taste _________________ games. 10. He is walking _________________ the road. 11. Smoking is injurious _________________ health. 12. He is not eligible _________________ this post. 13. She is adept ________ English. 14. He was informed _________________ his result.
LESSON NO 10
Conjunction
Definition
It is a word used for the joining one sentence to another. These words are used as Conjunction; and, but, or for, nor, yet, though, as before, since, if, while, unless, until, as soon as, as long as, etc.
Some conjunctions are used in pairs. They are also called Correlative Conjunctions. Some are called sub-ordinate conjunctions and some are called co-ordinate conjunctions.
Correlative Conjunctions
They are generally used together.
- Neither _________ nor
- Such _________ as
- Either _________ or
- Same _________ as
- So/as _________ as,that
- Although _________ yet
- Both _________ and
- Though _________ yet
- Whether _________ or
- Hardly _________ when
- Not only _________ but also
- Such _________ that
- No sooner _________ than
- lest _________ should
- Too _________ to
- Rather _________ than
- Other _________ than
Subordinating Conjunctions
They help to link or connect a dependent clause to an independent clause.
They are; that, who, which, when, where, why, how, whenever, while, unless, whoever, if, and because. They make complex sentence.
Coordinating Conjunctions
They help to link equal parts of a sentence including phrases and clauses.
They are; and, but, or, yet, and nor. They make compound sentences.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 10
Complete these sentences with suitable conjunctions.
- Although he tried _________________ he could not reach there.
- You will gain nothing _________________ you try.
- Take care of your books, _________________ books are your best friends.
- _________________ they saw a lion they ran away.
- No sooner did he enter the room _________________ it began to rain.
- Fakhira is _________________ intelligent as her sister.
- He is not so wise _________________ his brother.
- As you sow, _________________ shall you reap?
- He is _________________ weak that he cannot walk.
- Work hard _________________ you should fail.
- Neither does he sleep _________________ work.
- Not only Salma is foolish _________________ coward.
- Either Saima _________________ none can solve this sum.
- He is _________________ longer my friend.
- I will not stay here any _________________ .
- Although they were present there _________________ they could not help me.
- She is _________________ weak to walk.
- Stay here _________________ we come.
- _________________ you are physically unfit, you should not apply for this post.
- He tried agian and again _________________ in vain.
- He was so changed _________________ I could not recognize.
- Hardly we had reached there _________________ it began to rain.
- Listen carefully _________________ it is very important lecture.
- Both Sidra _________________ Uzama are intelligent girls.
- I have no other wealth _________________ my book.
LESSON NO 11
QUESTION WORDS
They are: why, when, where, which, what, how, many, how much, who, whose, and whom, etc.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 11
Complete these sentences with the help of these question words.
- _________________ does he go after classes?
- _________________ will you help me?
- _________________ will the train arrive?
- _________________ is this man? He has been sitting here since morning.
- _________________ do you ask my name?
- _________________ are you waiting for her?
- _________________ books are lying on the table?
- _________________ have you been? I have not seen you for so long.
- These are four boys, _________________ is your brother?
- _________________ many boys are going to take the examination this year?
- _________________ will bell the cat?
- _________________ milk is there in the cup?
- _________________ students are being promoted to the next class?
- _________________ do you want to see?
- _________________ are you doing here?
- _________________ are you carrying, this luggage?
- _________________ will you solve this sum?
- _________________ money have you invested in this business?
LESSON NO 12
ARTICLE
It is two types
Definite Article: The is a definite article and used in these cases.
- To point out or particularize a noun.
- The is used before a singular noun when it represents its class.
- The is used before adjective of quality. In this case, it becomes plural.
- The is used before the superlative degree of an adjective.
- The is used before a comparative degree in some cases.
- The is used before the name of rivers, newspapers, seas, ranges of mountains, ships, books, sects, religion, castes, families, etc.
- The is used before a proper noun when it is used as a common noun.
- If a common noun comes before a proper noun, the is used before it.
- The is used before the names of countries, provinces, cities, etc. If they are plural or have some geographical background.
- The is used before the nouns which are single.
- If we mention something or the thing known or the thing that has already been mentioned, the is used before it.
- The is used before school, mosque, market when we mean to say building.
- The is used before the names of nations.
- The is used before a proper, material or abstract noun when it is particularized or attributed to a particular place or person.
- It is used before the dates of the months.
- It is used before the adjective the same and after the adjective all and both.
- It is used before words denoting historical events.
- It is used before the words indicating weight and measure.
- The is used before directions.
- The is used before sky, sun, moon, star, earth.
It is not used before
- Man, woman when they represent their class.
- Before abstract and material nouns.
- Before the names of countries, cities and provinces.
- Before the name of a person.
- Before God, Hell, and Paradise.
- Before language, subjects, and diseases.
- Before the days of week, seasons.
Indefinite Article
A or an is an indefinite article. It generalizes a noun.
- A is generally placed before words beginning with letters other than a, e, I, o, u (vowels).
- A is used before a word beginning with a vowel but not giving the vowel sound.
- An is used before a word when it gives the sound of a vowel.
EXERCISE OF LESSON 12
Fill in the blanks with the, a or an
- Honesty is _________________ best policy.
- He is _________________ M.A.
- He is not _________________ good man.
- _________________ paradise lost is _________________ best book of classical poetry.
- _________________ king Akbar was very famous for his justice.
- _________________ earth revolves round _________________ sun.
- Which is _________________ longest river in Pakistan?
- What is _________________ latest news?
- He is _________________ Rustum of present age.
- _________________ rich should help _________________ needy.
- _________________ U.S.A is a large country.
- Her date of birth is _________________ sixteen of September.
- _________________ beauty of Helen is matchless.
- Oil is sold by _________________ liter.
- _________________ Muslim hates _________________ Jews.
- He is _________________ famous urologist.
- He is _________________ honourable man.
- He has a cow. _________________ cow is very beautiful.
- _________________ school is near _________________ mosque.
- _________________ mango is sweet.
- _________________ sun sets in _________________ west.
- There was _________________ thirsty crow.
- He is _________________ able man.
- _________________ watch you gave me has been lost.
- All _________________ girls are silent.
- _________________ more the sugar _________________ sweeter it is.
Exercise
Correct these sentences.
- The God is one.
- The man is mortal.
- The women are talkative.
- He is a honest man.
- Sun sets in west.
- We live near market.
- She is most beautiful girl.
- We should help the poors.
- The government has decided to set up an university.
- He plays the cricket.
Excercise
Complete with the, a, and an.
- _________________ unsurpur.
- _________________ smallest boy.
- _________________ honest worker.
- _________________ Pacific Ocean.
- _________________ leader Bhutto.
- _________________ West Indies.
- _________________ left.
- _________________ Maliks.
- _________________ Simpsons.
- _________________ Holy Quran.
- _________________ Old Testament.
- _________________ 7th of August.
- _________________ French Revolution.
- _________________ Unit.
- _________________ University.
- _________________ Eagle.
- _________________ Historical city.
- _________________ Heir.
- _________________ Honest man.
- _________________ west.

Fawas
July 8, 2021 at 3:02 amWallahi you have done a great job here please keep it up